Recent flooding events beginning May 20-21, 2024, in portions of Nebraska have some concerned about the need to replant corn when waters recede. It’s important to assess potential recovery before making replant decisions. This information pertains regardless of any disaster causing a potential replant situation (flooding, hail, frost damage, etc.) This information is revised from articles Lori Abendroth and Roger Elmore wrote several years ago.
Wait 5-7 days after emergence begins, then determine the current plant population.
Dig in the gaps to check the status of “missing” plants.
Scout in a zigzag pattern across the field to best represent its overall condition, including both better and worse areas.
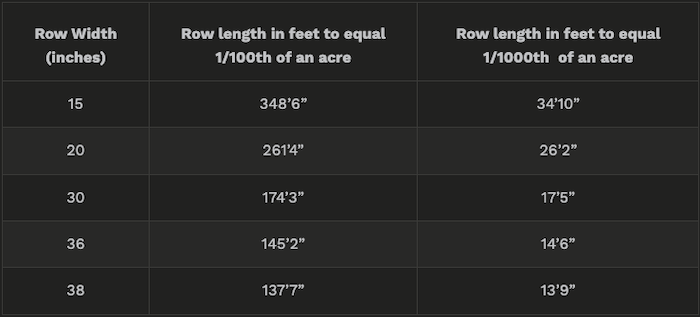
Table 1. Row length necessary to equal 1/100th and 1/1000th of an acre in various row widths.
To estimate surviving plant stands, count plants in at least three areas in affected fields. Consider increasing your accuracy by counting plants in 1/100 of an acre in contrast to just those in 1/1000 of an acre. Use Table 1 to determine the length of row necessary to achieve either a 1/100 or a 1/1000 of an acre sample. Multiply by either 100 or 1000 (depending on which area you counted) to determine the number of live plants per acre.
In the counted area, estimate whether severely injured plants will survive by checking the growing point and recovery. If the growing point is discolored and soft, the plant won’t survive. If it is firm and new green growth is emerging from it, it will most likely survive.
Consider plant stand uniformity (if there is uneven emergence). If uneven emergence is row to row, that is, most rows have emerged but some are not, replanting will likely not increase yield significantly.
If the delay in emergence is less than two weeks between the early and late-emerging plants, replanting may increase yields, but by only 5% or less. Replanting would likely not be economical. Yet, if one-half or more of the plants in the stand emerge three weeks later than the initial plant emergence, replanting may increase yields by about 10%.
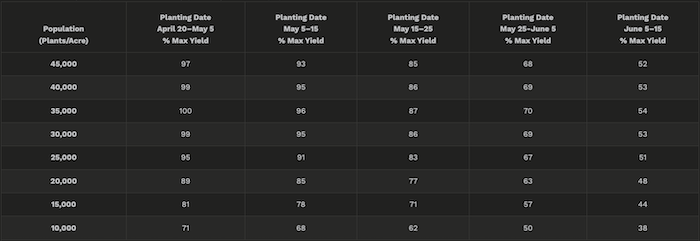
Calculate the expected yield from the existing stand using Table 2.
Table 2 summarizes planting date and plant population (final stand) relationships. Please see the examples below Table 2 for an explanation on using this table.
Table 2. Relative yield potential of corn by planting date and population.
With where we’re sitting today, if there are 25,000 plants per acre remaining and the field was initially planted on April 25, according to Table 2, the expected yield would be 95% of maximum. If you couldn’t replant until May 30, it may be better to leave the original stand than try to plant May 30 at 30,000 seeds per acre with an expected yield of nearly 69%.
If planting occurred on May 20 prior to this flooding event and a stand of 25,000 plants per acre remained with a yield potential of 83% of maximum, if you couldn’t replant until May 30, according to this chart, an expected yield potential would be nearly 69% of maximum yield. Consider your individual field situation and cost of replanting. Remember, there is no guarantee of getting a good stand with replanting and that late season insect and disease pressure may be greater in replanted fields. Also note that the yield reductions listed in this table may be greater than what actually occurs in 2024.
Note: Values based on preliminary Iowa research and modeling; 100% yield potential is estimated to occur with 35,000 plant population and early planting.
If several 4- to 6-foot gaps occur within the row, yields will be reduced an additional 5% relative to a uniform stand. Stand gaps of 16 to 33 inches will only reduce yield by 2%.
Ensure good weed management to aid for less competitive stands.
Remember, there is no guarantee of getting a good stand with replanting. Insect and disease pressure may be greater in replanted fields.
Estimate replant yield with Table 2. Use planting date and target plant population to estimate the yield potential of the replanted field.
Remember the concept of planting windows. (See CW articles with Nebraska data, historical Nebraska data, and Corn Belt data.) With that in mind, consider that the yield reductions listed in Table 2 may be greater than what may actually occur in 2024. Hybrids and genetics have improved and weather variation has increased since this table was developed. Anymore, an early to mid-May planting may result in full yield potential in some years.
NOTE: For example, in 2022, when widespread hailstorms impacted south and east-central Nebraska on June 14, corn wasn’t replanted till the end of June. In spite of sharing expected yields would be around 50% of maximum, yields of 200+ bushels/acre were still achieved (even with most of the corn being killed prematurely by frost). The yields may be due to that specific year, but genetics and environmental conditions have changed the optimal planting windows for corn. There is need for additional research using today’s hybrids and weather variability.
Estimate replanting costs.
The cost of replanting a field is often the deciding factor.
Make sure to include tillage, seed, fuel (for tillage and planting), additional pesticides, labor, etc. Don’t forget that the chance of fall frost is higher for late-planted corn.
Check with your seed dealer to see what hybrid seed is available and if there is any rebate or price reduction for replant situations. In general, there is not much of a reason to switch to earlier-season hybrids until early June. (See this CW article on when to change hybrids.)